











| LVT3: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | 1944 | Total acceptances | 2,962 |
| Manufacturers |
|
Crew | 3 men |
| LVT3: Dimensions | |||
| Combat weight | 38,600lbs 17,500kg |
Height | 119" 302cm |
| Length | 294" 745cm |
Width | 134" 340cm |
| Ground clearance | 19" 48cm |
||
| LVT3: Armament | |
| Type | Mount |
| .50cal M2HB MG | Mount at front of cargo area |
| Two .30cal M1919A4 MGs | One on each side of cargo area |
| LVT3: Armor | |
| None |
| LVT3: Automotive | |||
| Engine | Twin Cadillac Series 42; 16 cylinder (8/engine), 4 cycle, 90º vee gasoline | ||
| Horsepower | Net: 220@3,400rpm (110/engine) Gross: 296@3,200rpm (148/engine) |
Torque | Net: 488 ft-lb@1,200rpm (244/engine) Gross: 560 ft-lb@1,200rpm (280/engine) |
| Transmission | Twin Hydramatic, 4 speeds forward, 1 reverse | ||
| Steering | Controlled differential, steering levers | ||
| Brakes | Mechanical, external contracting | ||
| LVT3: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Torsilastic | 11 independently sprung/track | 3/track |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | 13-tooth front drive | Adjustable sprocket at rear of track | None |
| LVT3: Track | |||||
| Outside guide, double pin, extruded grousers | |||||
| Width | 12" 30cm |
Pitch | 5.5" 14cm |
Shoes/track | 103 |
| LVT3: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 17mph 27kph |
Max water speed | 6mph 10kph |
| Max fording depth | Floats | Cruising range | ~150mi, roads ~75mi, water ~240km, roads ~120km, water |
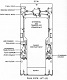
LVT3 can be differentiated from LVT2 and LVT4 by its cab, which was nearer the bow on LVT3. LVT3's cab had three windows, like that of LVT1. LVT3 also had a rear loading ramp, since its engines were mounted in either sponson. Applique armor could be added to LVT3, which decreased its 9,000lb (4,000kg) cargo capacity by 2,900lbs (1,300kg). The engines and transmissions of LVT3 were the same as the light tank M5 Stuart's. LVT3 was colloquially known as Bushmaster.
Beginning in 1949, 1,200 LVT3s were converted to LVT3(C) standard by the Long Beach Naval Shipyard. This involved mounting a .30cal MG in a turret on the vehicle roof and placing another .30cal MG in a ball mount in the cab right bow. A split aluminum cargo cover was installed which could be folded out of the way to on top of either sponson, escape hatches were fitted, and armor was added to the vehicles' sides. The bow of the LVT3(C) was extended to improve buoyancy. The LVT3(C) weighed 45,290lb (20,540kg) loaded; was 301.5" (765.8cm) long; 134.5" (341.6cm) wide; 121.5" (308.6cm) tall; had a ground clearance of 19.5" (49.5cm); and a ground pressure of 12.8psi (.900kg/cm²).













