| M88: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | 1960 | Total acceptances | 1,075 |
| Manufacturer | Bowen-McLaughlin-York Company | Crew |
|
| M88: Dimensions | |||
| Combat weight | 112,000lbs 50,800kg |
Height | 123" 312cm |
| Length with boom and spade in travel position | 325.5" 826.8cm |
Width over tracks | 135.0" 342.9cm |
| Tread | 107.0" 271.8cm |
Ground clearance | 17.0" 43.2cm |
| Ground pressure, zero penetration | 9.78psi .687kg/cm² |
||
| M88: Armament | ||||
| Type | Mount | Ammunition | Traverse | Elevation |
| .50cal M2HB MG | Flexible in cal. .50 AA mount 8367286 or 7046650 | 1,500 rounds | 360° (manual) |
Manual |
| Night vision | ||||
| Infrared periscopes M24 for driver and rigger | ||||
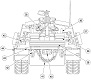
| M88: Armor | ||
| Assembly | ||
| Welding | ||
| Hull and cab | ||
| Rolled and cast homogeneous steel | ||
| Location | Thickness | Angle from vertical |
| Upper front | 1.25" 3.18cm |
26° |
| Lower front | 1.5" 3.8cm |
47° |
| Upper sides | .75" 1.9cm |
15° |
| Lower sides | 1.0" 2.5cm |
0° |
| Upper rear | 1.0" 2.5cm |
10° |
| Lower rear | 1.25" 3.18cm |
0° |
| Top | .75" 1.9cm |
90° |
| Front floor | 1.5" 3.8cm |
90° |
| Rear floor | 1.0" 2.5cm |
90° |
| M88: Automotive | |||||
| Engine | Continental AVSI-1790-6A; 12 cylinder, 4 cycle, 90° vee supercharged fuel-injected gasoline | ||||
| Horsepower | Net: 814@2,800rpm Gross: 980@2,800rpm |
Torque | Net: 1,600 ft-lb@2,100rpm Gross: 1,940@2,300rpm |
Fuel capacity | 425gal 1,610L |
| Transmission | Cross-Drive XT-1410-2A, 3 ranges forward, 1 reverse | ||||
| Steering | Mechanical, steering wheel | ||||
| Brakes | Multiple disc | ||||
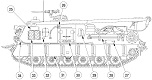
| M88: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Torsion bar | 6 independently sprung dual/track | 3 dual/track |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | 11-tooth rear drive | Dual compensating at front of track | On first 2 and last road wheels/track |
| M88: Track | |||||||
| T107 | |||||||
| Center guide, double pin, rubber chevron | |||||||
| Width | 28" 71cm |
Pitch | 7.09" 18.0cm |
Shoes/track | 84 | Ground contact length | 180" cm |
| M88: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 31mph 50kph |
Max trench | 103" 262cm |
| Max sideslope | 30% | Max grade | 60% |
| Max vertical obstacle | 42" 110cm |
Min turning diameter | Pivot |
| Max fording depth | 64" 160cm |
Cruising range | 222mi 357km |
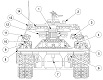
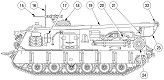
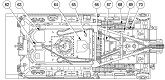
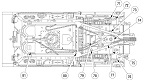
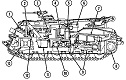
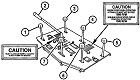
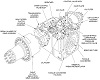
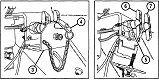
The M88 shared its powertrain with the heavy recovery vehicle M51. An hydraulically-controlled stabilizing spade that could also be used as a dozer blade was mounted on the vehicle's front. The 90,000lb (41,000kg)-capacity main winch was installed below the crew floor, and was fed with 200' (61m) of 1¼" (3.18cm) cable. An A-frame boom was mounted on top of the cab, supported in the operating position by a fifty-three foot (16m) long 1¼" (3.18cm) wire rope stayline, enabling a 50,000lb (23,000kg) live-boom lifting capacity with the spade lowered. With the spade raised, the boom capacity was limited to 12,000lb (5,400kg). Its hoist winch was supplied with 400' (120m) of ⅝" (1.59cm) cable. The hoist winch had a maximum single-line capacity of 12,500lb (5,670kg), and a 50,000lb (23,000kg) pull using a four-part line. The boom could lift a load 19' (5.8m) high with an 8-foot (2.4m) reach, or 25' (7.6m) high with a 4-foot (1.2m) reach. Suspension lockout blocks were able to be fitted to the front road wheel on each side for use during operations requiring lifting and carrying loads of 6-20 tons (5,400-18,000kg).


















| M88A1: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | June 1975 | ||
| Manufacturer | Bowen-McLaughlin-York Company | Crew |
|
| M88A1: Dimensions | |||
| Combat weight | 112,000lbs 50,800kg |
Height | 123" 312cm |
| Length | 325.5" 826.8cm |
Width over tracks | 135.0" 342.9cm |
| Tread | 107.0" 271.8cm |
Ground clearance | 17.0" 43.2cm |
| Ground pressure, zero penetration | 10.9psi .765kg/cm² |
||
| M88A1: Armament | ||||
| Type | Mount | Ammunition | Traverse | Elevation |
| .50cal M2HB MG | Flexible in cal. .50 AA mount 8367286 or 7046650 | 1,500 rounds | 360° (manual) |
Manual |
| Night vision | ||||
| Infrared periscopes M24 or M24A1 for driver and rigger | ||||
| M88A1: Armor | ||
| Assembly | ||
| Welding | ||
| Hull and cab | ||
| Rolled and cast homogeneous steel | ||
| Location | Thickness | Angle from vertical |
| Upper front | 1.25" 3.18cm |
26° |
| Lower front | 1.5" 3.8cm |
47° |
| Upper sides | .75" 1.9cm |
15° |
| Lower sides | 1.0" 2.5cm |
0° |
| Upper rear | 1.0" 2.5cm |
10° |
| Lower rear | 1.25" 3.18cm |
0° |
| Top | .75" 1.9cm |
90° |
| Front floor | 1.5" 3.8cm |
90° |
| Rear floor | 1.0" 2.5cm |
90° |
| M88A1: Automotive | |||||
| Engine | Continental AVDS-1790-2DR; 12 cylinder, 4 cycle, 90° vee supercharged diesel | ||||
| Horsepower | Net: 642@2,400rpm Gross: 750@2,400rpm |
Torque | Net: 1,585ft-lb@1,80000rpm Gross: 1,720@1,800rpm |
Fuel capacity | 400gal 1,500L |
| Transmission | XT-1410-4, 3 ranges forward, 1 reverse | ||||
| Steering | Mechanical, steering wheel | ||||
| Brakes | Multiple disc | ||||
| M88A1: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Torsion bar | 6 independently sprung dual/track | 3 dual/track |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | 11-tooth rear drive | Dual compensating at front of track | On first 2 and last road wheels/track |
| M88A1: Track | |||||||
| T107 | |||||||
| Center guide, double pin, rubber chevron | |||||||
| Width | 28" 71cm |
Pitch | 7.09" 18.0cm |
Shoes/track | 84 | Ground contact length | 180" cm |
| M88A1: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 26mph 42kph |
Max trench | 103" 262cm |
| Max grade | 60% | Max vertical obstacle | 42" 110cm |
| Min turning diameter | Pivot | Max fording depth | 56" 140cm |
| Cruising range | ~300mi ~480km |
||
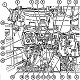
The dieselization of the US military's vehicle fleet resulted in the AVDS-1790-2DR engine being installed in the M88, yielding the M88A1. The auxiliary generator and crew heater were also changed to diesel-powered units. The boom lift height at 8' (2.4m) of reach was 270.5" (687.1cm), and at 4' (1.2m) reach was 301.50" (765.81cm). The boom capacity with the spade stowed was 6 tons (5,400kg) without the suspension locked and 20 tons (18,000kg) with the suspension locked. With the spade deployed the boom capacity increased to 25 tons (23,000kg).
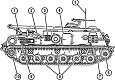
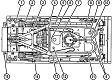
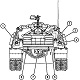
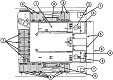








| M88A2: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | July 1997 | ||
| Manufacturers |
|
Crew |
|
| M88A2: Dimensions | |||
| Combat weight | 139,600lbs 63,320kg |
Height | 117" 297cm |
| Length | 340.0" 863.6cm |
Width | 144" 366cm |
| Tread | 107.0" 271.8cm |
Ground clearance | 17.0" 43.2cm |
| Ground pressure, zero penetration | 13.39psi .934kg/cm² |
||
| M88A2: Armament | ||||
| Type | Mount | Ammunition | Traverse | Elevation |
| .50cal M2HB MG | Flexible in cupola AA mount | 1,300 rounds | 360° (manual) |
Manual |
| Night vision | ||||
| Passive night viewer AN/VVS-2(V)1A and Driver's Viewer Enhancer | ||||
| M88A2: Armor | ||
| Assembly | ||
| Welding | ||
| Hull and cab | ||
| Rolled and cast homogeneous steel |
| M88A2: Automotive | |||
| Engine | Continental AVDS-1790-8CR; 12 cylinder, 4 cycle, 90° vee turbosupercharged diesel | ||
| Horsepower | Gross: 1,050@2,400rpm | Fuel capacity | 413gal 1,560L |
| Transmission | XT-1410-5A, 3 ranges forward, 1 reverse | ||
| Steering | Mechanical, steering wheel | ||
| Brakes | Multiple disc | ||
| M88A2: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Torsion bar | 6 independently sprung dual/track | 3 dual/track |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | 11-tooth rear drive | Dual compensating at front of track | On first 2 and last road wheels/track |
| M88A2: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 25mph 40kph |
Max trench | 102" 259cm |
| Max sideslope | 30% | Max grade | 60% |
| Max vertical obstacle | 42" 110cm |
Min turning diameter | Pivot |
| Max fording depth | 56" 140cm |
Cruising range | 314mi 505km |
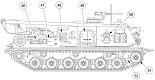
The M88A1 began to struggle with the introduction of the M1 Abrams and especially the M1A1, which weighed ~28,000lb (~12,700kg) more than the M60 that the M88 had been initially intended to recover: two M88A1s were required to safely tow an Abrams tank. Thus, the M88A2 Heavy Equipment Recovery Combat Utility Lift and Evacuation System (HERCULES) was introduced in July 1997. The M88A2 used the hull of the M88A1, but featured an improved powertrain making more power; additional armor including ballistic skirts; stronger winching and hoisting capacities; and suspension, brake, and hydraulic system improvements. The main winch has a 140,000lb (63,500kg) capacity and 280 usable feet (85m) of 1.4" (3.6cm) cable and the boom hoist capacity has increased to 35 tons (32,000kg). A 3-ton (2,700kg) auxiliary winch was added to assist with the outlaying of the main winch cable, and this is provided with 654 usable feet (199m) of .375" (.953cm) cable.