






















| M40: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | February 1945 | Total acceptances | 418 (24 converted to 8" HMC M43) |
| Manufacturer | Pressed Steel Car Co. | Crew | 8 men |
| M40: Dimensions | |||
| Combat weight | 81,000lbs 37,000kg |
Height over gun mount | 130" 330cm |
| Length without gun | 280.4" 712.2cm |
Gun overhang forward | 68" 170cm |
| Width | 124" 315cm |
Tread | 101" 257cm |
| Ground clearance | 17" 43cm |
Fire height | 102" 259cm |
| Ground pressure, zero penetration | 10.7psi .751kg/cm² |
||
| M40: Armament | ||||
| Type | Mount | Ammunition | Traverse | Elevation |
| 155mm Gun M1A1 or M2 | M13 on rear of chassis | 20 rounds | 36° (18° left and right; manual) |
+45° to -5° (manual) |
| Aiming equipment | ||||
| Panoramic telescope M12 or M12A7C and telescope M69F for gunner; elbow telescope M16A1F for cannoneer no.1 | ||||
| M40: Armor | ||
| Assembly | ||
| Welding | ||
| Hull | ||
| Rolled and cast homogeneous steel | ||
| Location | Thickness | Angle from vertical |
| Upper front | .5" 1.3cm |
58° |
| Lower front | 4.25" to 2.0" 10.8cm to 5.1cm |
0° to 46° |
| Upper sides | .5" 1.3cm |
0° |
| Lower sides | 1.0" 2.5cm |
0° |
| Rear | .5" 1.3cm |
0° |
| Top | .5" 1.3cm |
85° |
| Front floor | 1.0" 2.5cm |
90° |
| Rear floor | .5" 1.3cm |
90° |
| Gun shield | .5" 1.3cm |
~45° |
| M40: Automotive | |||||
| Engine | Continental R975 C4; 9 cylinder, 4 cycle, static radial, supercharged gasoline | ||||
| Horsepower | Net: 400@2,400rpm Gross: 460@2,400rpm |
Torque | Net: 940 ft-lb@1,700rpm Gross: 1025 ft-lb@1,800rpm |
Fuel capacity | 215gal 814L |
| Transmission | Synchromesh, 5 speeds forward, 1 reverse | ||||
| Steering | Controlled differential, steering levers | ||||
| Brakes | Mechanical, external contracting | ||||
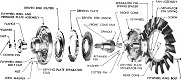
| M40: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Horizontal volute spring | 3 bogies/track; 2 dual wheels/bogie |
2 dual/track, 3 single/track |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | 13-tooth front drive | Dual adjustable at rear of track | One on each bogie |
| M40: Track | |||||||
| T66 | |||||||
| Center guide, single pin, cast, steel | |||||||
| Width | 23" 58cm |
Pitch | 6" 15cm |
Shoes/track | 86 | Ground contact length | 164" 417cm |
| T80 | |||||||
| Center guide, double pin, rubber and steel | |||||||
| Width | 23" 58cm |
Pitch | 6" 15cm |
Shoes/track | 86 | Ground contact length | 164" 417cm |
| T84 | |||||||
| Center guide, double pin, rubber | |||||||
| Width | 23" 58cm |
Pitch | 6" 15cm |
Shoes/track | 86 | Ground contact length | 164" 417cm |
| M40: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 21mph sustained 24mph dash 34kph sustained 39kph dash |
Max trench | 92" 230cm |
| Max grade | 60% | Max vertical obstacle | 24" 61cm |
| Min turning diameter | 83' 25m |
Max fording depth | 40" 102cm |
| Cruising range | ~100mi, roads ~160km, roads |
||
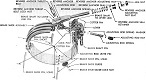
The hull and chassis of the M40 were based on that of the late-production medium tank M4. The hull was lengthened and widened and used HVS suspension. The drivers were provided with individual viewing cupolas. The layout of the M40 was similar to the 155mm GMC M12 in that the engine was moved forward to behind the driving compartment, the gun was mounted at the rear of the vehicle, and the M40 was open-topped except for the driving compartment.





























