
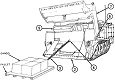



| M9: General | |||
| Date of first acceptance | 1986 | Total acceptances | 620 |
| M9: Manufacturer | BMY Combat Systems | Crew | 1 man |
| M9: Dimensions | |||
| Net weight | 39,000lbs 17,700kg |
Height above cupola | 105" 267cm |
| Length | 245" 622cm |
Width with extensions removed | 110" 280cm |
| Tread | 88.00" 223.5cm |
Ground clearance | 13" 33cm |
| Ground pressure, zero penetration | 9.5psi .67kg/cm² |
||
| M9: Armament |
| None |
| M9: Armor |
| Assembly |
| Welding and bolting |
| Operator's station |
| Aluminum armor, steel and aramid laminate plates |
| M9: Automotive | |||
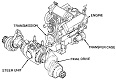
| Engine | Cummins V903C; eight cylinder, 4 cycle, vee diesel | ||
| Horsepower | 295@2600rpm | Fuel capacity | 134gal 507L |
| Transmission | Clark 13.5 HR 3610-2, 6 speeds forward, 2 reverse | ||
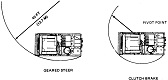
| Steering | Geared steer and clutch-brake | ||
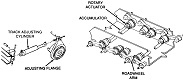
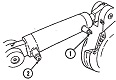
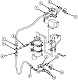
| M9: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Track return rollers |
| Hydropneumatic | 4 individually sprung dual/track | Flat track |
| Drive sprockets | Idlers | Shock absorbers | Rear drive | Front road wheels act as idlers | None |
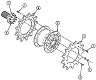
| M9: Track | |||
| Single pin, rubber padded steel | |||
| Width | 18" 46cm |
Ground contact length | 105" 267cm |
| M9: Performance | |||
| Max level road speed | 30mph 50kph |
Max water speed | 3mph 5kph |
| Max trench | 62" 160cm |
Max sideslope with 18,000lbs (8,200kg) in bowl | 40% |
| Max grade with 18,000lbs (8,200kg) in bowl | 60% | Angle of approach (maximum) | 29° |
| Angle of departure (maximum) | 27° | Max vertical obstacle | 18" 46cm |
| Min turning diameter | Pivot | Max fording depth | Floats |
| Cruising range | ~230mi, roads ~370km, roads |
||
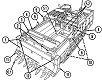
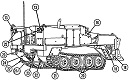
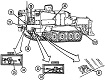
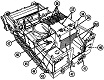
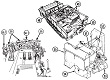
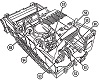
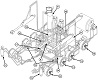
The US Army's search for an armored combat earthmover, or universal engineering tractor, spanned thirty years. The resulting M9 ACE featured a front-mounted dozer blade, behind which is an 8.7 cubic yard (6.7m3) scraper bowl. For jobs requiring a heavier machine, the blade could be raised and the bowl could be filled with dirt, bringing the vehicle's weight up to 57,000lbs (26,000kg). Originally, a 25,000lb (11,000kg) winch was mounted in the lower rear hull, beneath the engine and transmission. This was replaced by a 35,000lb (16,000kg) model with 165' ±2' (50.3m ±.6m) of ¾" (1.9cm) wire rope. The dozer blade was positioned by adjusting the hydropneumatic suspension. The operator was stationed at the rear of the vehicle and was provided with a cupola containing eight vision blocks. After the vehicle had entered service, modifications were performed that increased the vehicle's weight to the point that swimming was no longer feasible. The amphibious requirement was therefore dropped, and its maximum fording depth was 36" (91cm).