| M289: General | |||||
| Date of first acceptance | 1953 | Crew |
|
||
| M289: Dimensions | |||
| Weight with MGR-1A rocket | 47,713lbs 21,643kg |
Height with MGR-1A rocket | 151½" 384.8cm |
| Length with rocket | 541" 1,370cm |
Width | 120" 305cm |
| Tread | 81" 205cm |
Wheelbase | 215" 546cm |
| Road clearance | 13" 33cm |
||
| M289: Armament | ||||
| Type | Mount | Ammunition | Traverse | Elevation |
| 762mm Rocket MGR-1A, MGR-1B, or MGR-1C | 762mm rocket launcher 8417300 | 1 rocket | 30° (15° left and right; manual) |
+60° to +5° (manual and power) |
| Aiming equipment | ||||
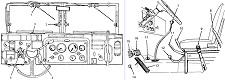
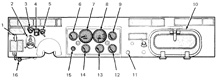
| Panoramic telescope M12A7C for gunner | ||||
| M289: Armor |
| None |
| M289: Automotive | |||||
| Engine | Continental R6602; 6 cylinder, 4 cycle, inline gasoline | ||||
| Horsepower | 196@2,800rpm | Torque | 480lb-ft@1,200rpm | Fuel capacity | 78gal 295L |
| Transmission | Spicer Model 6352 synchromesh, 5 speeds forward, 1 reverse | ||||
| Steering | Steering wheel | ||||
| Brakes | Air-assisted hydraulic | ||||
| M289: Suspension | ||
| Type | Road wheels | Shock absorbers |
| Semi-elliptic leaf spring | 3/side | On front wheels |
| M289: Performance | |||
| Turning radius | 54' 16m |
Max fording depth | 30" 76cm |
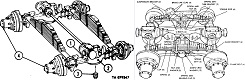
The M289 was used to launch the Honest John series of free-flight, fin-stabilized surface-to-surface rockets. It was based on the 5-ton 6x6 truck M139C, which was an extended-wheelbase version of the 5-ton 6x6 truck M39 with a modified front cross-member and high-reduction axles to increase tractive power. The chassis designation was changed to M139D when equipped with the 762mm rocket launcher and bracket supports for five screw-type leveling jacks. A Rockwell T-138 2-speed transfer case helped account for heavy or light load conditions, and the M139D was fitted with a 1.02:1 rear axle. The launcher rail was 508" (1,290cm) long.
The solid-fueled 762mm rocket M31 Honest John was the Army's first tactical nuclear rocket. Two M7 spin motors helped ensure stabilization after launch. The first XM31 rockets were delivered by the Douglas Aircraft Company in January 1953, and the first production system in January 1954. Standardization as the M31 occurred on 1 September 1953. The warhead could contain 412lb (187kg) or 1,500lb (680kg) of high-explosive, a W-7 nuclear device with a yield of 2-40 kilotons, or a W-31 boosted fission warhead with a yield of up to 40 kilotons. Three hundred W-7 warheads were stockpiled from 1954-1960, and 1,650 W-31s were produced from October 1959 to December 1961. The M31A1 rocket, first produced in 1954, was propelled by an improved M3A1 rocket motor; similarly the M31A1C, introduced in late 1956, used a rocket motor M3A1C. The M31A2 from 1959 was powered by the rocket motor M3A2. The M3A1C and M3A2 rocket motors had firing-temperature limits of 0-120°F (-17 to 49°C) compared to the M3A1's 0-100°F (-17 to 38°C). The XM50 replaced the M31A2 in production in 1960, with the first rockets reaching units in 1961. The XM50 was standardized as the M50 in December 1962, and had a lighter (3,103lb [1,408kg] versus the M3A1's, M3A1C's, and M3A2's 4,109lb [1,864kg]) and stronger rocket motor M66 as well as shorter fins. These changes enhanced the system's accuracy and extended the range from 15.4 miles to 30 miles (24.8km to 48km). The rockets were renamed in June 1963, with the M31 series becoming MGR-1A, the M50 changing to MGR-1B, and the improved M50A1 designated MGR-1C. Production of the M31 series totaled 7,799 rockets, and M50 series production reached 7,089. The M289 was 533½" (1,355cm) long overall, 150¾" (382.91cm) high, and weighed 46,519lb (21,101kg) with an MGR-1B rocket loaded. The Honest John was assigned to the National Guard as the Lance missile came online, and all Honest John rocket motors, launchers, and ancillary ground equipment were declared obsolete on 9 July 1982.
Top















References
- TM 9-500 C3 Data Sheets for Ordnance Type Materiel. Washington, DC: Headquarters, Department of the Army, 12 October 1966.
- TM 9-2320-211-10 C2 Operator's Manual for Truck, 5-ton, 6X6, M39 Series Truck Chassis: 5-ton, 6X6, M40, M40A1, M40A1C, M40A2C, M61, M61A1, M61A2, M63, M63A1, M63A2, M63C, M63A1C, M63A2C, M139, M139A1, M139F, M139A1F, M139A2F; Truck, Cargo: M54, M54A1, M54A2, M54A1C, M54A2C, M55, M55A2; Truck, Dump: M51, M51A1, M51A2; Truck, Tractor: M52, M52A1, M52A2; Truck, Tractor, Wrecker: M246, M246A1, M246A2; Truck, Van, Expansible: M291A1, M29A1D, M291A2D; Truck, Wrecker, Medium: M62, M543, M543A1, M543A2; Truck, Stake, Bridge Transporting: M328A1; Truck, Bolster: M748A1. Washington, DC: Headquarters, Department of the Army, 2 November 1989.
- TM 9-2320-211-20 C3 Organizational Maintenance Manual for Truck, Chassis: 5-ton, 6X6, M39, M39A2, M40, M40A1, M40A2, M40A1C, M40A2C, M61 , M61A1 , M61A2, M63, M63A1, M63A2, M63C, M63A1C, M63A2C, M63A1D, M63A2D, M139A1, M139A2, M139C, M139A2C, M139D, M139A2D, M139F, M139A1F, M139A2F; Truck, Cargo: M41, M41A2, M54, M54A1, M54A2, M54A1C, M54A2C, M55, M55A1, M55A2; Truck, Dump: M51, M51A1, M51A2; Truck, Tractor: M52, M52A1, M52A2; Truck, Tractor, Wrecker: M246, M246A1, M246A2; Truck, Van, Expansible: M291A1, M291A2, M291A1C, M291A2C, M291A1D, M291A2D; Truck, Wrecker, Medium: M62, M543, M543A1, M543A2; Truck, Bridging: M139, M328A1, M328A2; Truck, Logging: M748A1, M748A2. Washington, DC: Headquarters, Department of the Army, 28 April 1982.
- FM 6-60 C2 Field Artillery Rocket Honest John with Launcher M289. Washington, DC: Headquarters, Department of the Army, 22 July 1969.
- Crismon, Fred W. U.S. Military Wheeled Vehicles. Minneapolis: Victory Publishing, Ltd., 2001.
- Parsch, Andreas. "Douglas MGR-1 Honest John." Designation-Systems.Net. 11 January 2002. Accessed 19 September 2024 <http://designation-systems.net/dusrm/r-1.html>.
- "Honest John." Redstone Arsenal Historical Information. Accessed 24 September 2024 <https://history.redstone.army.mil/miss-honestjohn.html>.
- Sublette, Carey. "List of All U.S. Nuclear Weapons." The Nuclear Weapon Archive: A Guide to Nuclear Weapons. 30 March 2023. Accessed 19 September 2024 <https://nuclearweaponarchive.org/Usa/Weapons/Allbombs.html>.
- Air Force Instruction 16-401(I), Army Regulation 70-50, Navy AIRINST 13100.16. Designating and Naming Defense Military Aerospace Vehicles. 14 April 2005.